When you think of the word "lean," you might picture a working car. A lean vehicle is designed for efficiency, using less fuel while delivering top performance.
In project management, this concept of excess translates into project defects. These defects can lead to scope creep and ultimately diminish the overall value of your project. Just like a car that uses more fuel than necessary, a project burdened by waste can drift off course, ultimately compromising its success.
The main motive for adopting a lean approach is to minimize waste and maximize value at every stage of your project. In this article, we’ll dive into what lean project management is all about. We’ll also explore how you can leverage this Agile methodology to boost your productivity and streamline your processes.
250px|700px|reset
How Was the Lean Project Management Methodology Created?
The lean project management methodology originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS), developed by Japanese engineers at Toyota between 1948 and 1975. Originally, TPS was a way to improve production efficiency, enhance collaboration with suppliers, and minimize waste. Over time, these principles laid the groundwork for what we now call lean methodology.
In his book "The Toyota Way," Dr. Jeffrey K. Liker outlines how companies can apply the TPS principles beyond manufacturing, showing how lean practices help eliminate waste and maximize efficiency in a variety of industries. His work serves as a practical guide for companies striving to improve operations using lean principles.
John Krafcik first introduced the term "lean" to project management in his 1988 article, "Triumph of the Lean Production System." Krafcik's research at MIT Sloan School of Management led to the influential book "The Machine That Changed the World," which further popularized the lean approach.
Since then, lean project management has influenced a variety of other methodologies, such as Agile, Kanban, and Scrum. These approaches share the same focus on efficiency, minimizing waste, and maximizing value.
5 Principles of Lean Project Management
Lean project management revolves around five fundamental principles, each of which serves to minimize waste and maximize value for stakeholders.
When approached correctly, these principles work together to streamline workflows, ensuring the project remains on scope and meets critical success factors.
Here’s a rundown of these principles, reimagined to give you a fresh perspective on how they all fit together seamlessly.
- Identify Value
- Identify Value
Everything in lean project management starts with knowing the value you're supposed to deliver.
Before you can start cutting inefficiencies, you need to know what you're building and who it's for. Internal stakeholders (like shareholders) are vested in the project's success, while external stakeholders are the customers buying your product. Recognizing what’s important to them is key to defining value.
For instance, internal stakeholders might see value in improving operational efficiency, while for external customers, the value could be as simple as solving a problem or making their life easier.
- Map the Value Stream
- Map the Value Stream
Mapping the value stream is a key concept in lean project management. Essentially, it’s about using a visual map to compare how your project flows now versus how you’d ideally like it to flow from start to finish. This method helps you uncover where waste is happening so that you can tackle inefficiencies head-on.
Toyota, one of the pioneers in lean manufacturing, identified several categories of waste that can sneak into any project. These concepts are relevant not just for manufacturing but for various industries, especially when dealing with digital products. Here’s a breakdown:
- Overproduction (Overburdening With Features): Adding more features than necessary is similar to manufacturing more than you need. It can lead to increased costs, like extra storage, wasted time, and unnecessary inventory piling up. This could look like building features no one asked for in the software world.
- Inventory (Poorly Managed Backlog): Think of inventory waste as the cost of holding onto unfinished work. Whether it’s a poorly managed backlog or incomplete tasks, this creates extra costs from storing materials or spending time to complete what’s left. These hidden costs build up over time.
- Motion (Switching Tasks): Motion waste comes from all the unnecessary movement in a project—whether it’s people or software processes. For example, constantly switching between tasks can add up quickly. Did you know the average worker switches tasks about 10-20 times an hour? And with this switching, it takes them 25 minutes to go back to the original task at hand every time.
- Defects (Technical Debt): Any product or service defect leads to wasted resources because of costly repairs or materials being lost. For digital projects, this often comes in the form of technical debt, which is time lost fixing bugs that could’ve been avoided.
- Over-processing (Costly Tools): Over-processing occurs when you invest in upgrading something that doesn’t need it, leading to extra costs. Similarly, using overly expensive tools that aren’t essential can drain your resources unnecessarily.
- Waiting: Delays can be costly, especially when a team’s progress is held up because of waiting on other processes. The longer you wait for deliverables, the more waste builds up, impacting the timeline and budget.
- Transport: Transport waste refers to the unnecessary movement of materials or information across different phases. Although this often relates to physical products, it can also apply to transporting digital assets or files, which can slow things down.
- Fragmented Teams: Poor communication and lack of strong collaboration lead to fragmented teams, resulting in miscommunication, extra meetings, and wasted time. These delays can drive up costs and lower overall project efficiency.
Research indicates that 11.4% of investments are lost due to poor project performance, yet only 25% of companies leverage comprehensive project management software.
To minimize project waste, it’s essential to identify these issues and adopt effective project management tools to optimize your workflows. By mapping out the value stream, you’ll gain clear insight into these potential inefficiencies.
This is why value stream mapping is crucial in lean project management—it. It shows you exactly where the gaps are, allowing you to eliminate waste and improve the quality of the final product.
- Create Flow
- Create Flow
After pinpointing inefficiencies, it’s time to clear the bottlenecks. Here, the focus shifts to optimizing your process flow.
Breaking down your project into manageable stages allows you to reorganize where needed, removing unnecessary steps and ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Plus, regular check-ins and milestones ensure new inefficiencies don’t sneak in during the project. If, for instance, a backlog was causing delays, this is the stage where you address the issue head-on.
- Establish Pull
- Establish Pull
The pull system helps keep tasks flowing smoothly, step by step. It’s a method that originated in manufacturing but works just as well in fields like software development or service industries.
The idea is only to move tasks forward when the previous stage is done, avoiding overproduction and excess work. It’s like having a clear hand-off point where everyone knows the baton is ready to be passed. This way, work doesn’t pile up, and teams stay synchronized.
- Continuous Improvement
- Continuous Improvement
The last principle, but certainly not the least, is about always striving to improve.
Lean project management isn’t a one-off process. The world changes, and so do your stakeholders’ needs, so you’ll need to keep revisiting your processes. Constantly looking for waste, rethinking your workflow, and tweaking things as you go ensures you’re always moving toward a better, more efficient way of working. It’s all about embracing the idea that there’s always room for improvement.
In lean project management, everything ties together. Once you apply these principles, you’ll notice how each builds on the other, helping your project flow more smoothly and efficiently while keeping everyone—internal and external—satisfied.
Lean Project Management Tools
Businesses often need to leverage lean project management tools to enhance product development efficiency. These tools are designed to streamline workflows, minimize waste, and boost team productivity, all while delivering more value to customers.
Below are some of the key methodologies you can explore:
Deming Cycle (PDCA)
Originally developed by Dr. W. Edwards Deming in the 1950s, the Deming Cycle—also known as the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle—refines an earlier problem-solving process.
It provides a structured, step-by-step approach that helps businesses make continuous adjustments while improving workflows and operations.
One of the best parts about using this cycle is that it allows you to test changes on a small scale first. This way, you can ensure that any tweaks or shifts in workflow are effective before rolling them out across the board. It’s like dipping your toes in the water before diving in—more controlled, less risk.
Let’s break down the four steps of the PDCA cycle and see how each one contributes to this ongoing process:
Step 1: Plan
In this initial phase, the focus is on identifying the issues and understanding how to tackle them. By analyzing the current workflow, you can identify areas that need improvement.
Once you’ve identified the problem, it's time to map out a plan of action, including what data to collect and how it will be reviewed. Think of it like setting the foundation for a house—everything else depends on getting this part right.
Step 2: Do
Now that you have a plan, it’s time to implement it. This step involves making the necessary changes to your workflow or processes.
Documenting everything—successes, challenges, and any unexpected outcomes is also important.
If something doesn’t go according to plan, this documentation will be vital for the next step. For example, think about building the house; you’re applying the blueprint but might need to adjust along the way.
Step 3: Check
After the changes are in place, it’s crucial to check if they’re working as intended.
Here, you collect data and analyze how well the new processes perform. Did they meet the goals set in the planning stage?
If everything’s running smoothly, you can move to the next step.
If not, it’s back to the drawing board. This is like inspecting your newly built house—if something is off, you want to catch it before it becomes a bigger problem.
Step 4: Act
In the final phase, you either standardize the successful changes or revisit your plan for further refinement.
- If the new process is effective, integrate it into your workflow to become the new standard.
- If it’s not, adjust and repeat the cycle until you find a solution that works.
It’s like moving into that fully-built house—you’re now set, but always ready for renovations if needed.
By following the PDCA cycle, businesses can make minor, manageable improvements that eventually lead to big results.
Lean Six Sigma Project Management (DMEDI)
Lean Six Sigma combines lean management principles with Six Sigma's data-driven approach, providing a robust framework to optimize workflows.
This approach follows five main steps, known collectively as DMEDI:
- Define: Clearly outline the project scope and objectives.
- Measure: Establish the metrics you'll use to track the project's success.
- Explore: Investigate potential avenues for process improvement.
- Develop: Create a solid project plan that addresses the problems identified.
- Implement: Put the plan into action and monitor its effectiveness.
Lean Six Sigma also incorporates various analytical tools, such as:
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): A visual tool that helps you pinpoint waste across different stages of your process.
- Customer Feedback Surveys: Gathering direct insights from customers to highlight issues and enhance product value.
- Gantt Charts: These are bar-like visual aids that can help you track key milestones.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): This technique digs into the underlying causes of recurring problems.
- Kanban Boards: By mapping out your tasks and setting limits on work in progress, Kanban boards help teams visualize and control their workflows.
Selecting the suitable lean management method often depends on your specific industry, the type of product you're developing, and your team's needs.
A combination of these approaches works best, and modern project management software can help you integrate these tools seamlessly into your processes.
Why Lean Management Is Important
Industries like IT, construction, and even education have embraced lean management principles for a reason. By focusing on eliminating inefficiencies, lean project management helps companies deliver more value to customers and streamline their operations.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
The benefits are clear and go beyond just cutting costs—they foster a more innovative and agile environment.
- Increased Innovation
- Increased Innovation
One key advantage of lean management is its ability to fuel creativity and innovation. When team members aren’t bogged down by inefficient processes, they have more freedom to brainstorm and experiment with new ideas.
For instance, think about how simplifying a routine task could spark an unexpected breakthrough in product development.
- Low Waste
- Low Waste
At the heart of lean management is minimizing waste, whether it’s physical waste or inefficiencies like overproduction. In this case, it’s about cutting down on unnecessary steps that slow things down.
Picture an assembly line running smoother because you've reduced waiting times between production phases—faster results with less clutter.
- Better Customer Service
- Better Customer Service
Lean practices also make it easier to meet customer expectations without over-delivering or overcomplicating the process.
The goal is to give your customers exactly what they need, without any extra frills. It’s like customizing a meal perfectly to someone’s taste, ensuring satisfaction without adding unnecessary items.
- Faster Lead Times
- Faster Lead Times
By reducing bottlenecks, lean management naturally shortens lead times, allowing teams to respond faster and complete projects quicker.
For example, if you take the express lane at a grocery store—you move through the process without unnecessary delays.
- Top-Notch Products
- Top-Notch Products
Another significant benefit is improved product quality.
Lean methodology often involves continuous quality checks, catching issues before they become bigger problems. Think of it as a careful inspection during every stage of the process, preventing defects and ensuring customers get top-tier products.
- Greater Inventory Management
- Greater Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is crucial to avoiding project setbacks, and lean management helps teams monitor inventory more efficiently.
This not only prevents shortages but also reduces overstocking, much like a well-organized pantry ensures you have just what you need without excess.
- Heightened Stakeholder Satisfaction
- Heightened Stakeholder Satisfaction
All the benefits we've discussed will ultimately enhance stakeholder satisfaction, both internally and externally.
If you do project management the right way, it will significantly improve the workflows of internal stakeholders, making their lives much more manageable. Meanwhile, external stakeholders will enjoy high-quality solutions with fewer revisions needed.
Ultimately, whether you're working with internal or external stakeholders, adopting a lean mindset can simplify your processes and build a more productive project team. It’s all about doing more with less, improving efficiency, and delivering higher value at every step.
Improve Your Workflow with Lean Project Management
By implementing lean principles, you can create smoother workflows and drive better results for your team.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
Below are some actionable steps to introduce lean thinking into your project management processes:
- Identify and Eliminate Waste
- Identify and Eliminate Waste
Lean methodology focuses on cutting out waste, whether that’s time, resources, or unnecessary steps in the workflow. Start by mapping out your processes and identifying where delays or inefficiencies occur.
Once you’ve pinpointed these bottlenecks, you can work on removing or streamlining them. For instance, if waiting for approvals causes delays, consider using automation tools to speed up this process.
- Adopt Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
- Adopt Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Kaizen, which means “continuous improvement,” is a core lean principle. Foster a culture where your team constantly finds small ways to improve workflows. Implement ongoing feedback loops to identify specific areas for improvement.
Moreover, holding weekly reflection meetings allows the team to discuss what worked and what didn’t, fostering an environment of open communication. These regular discussions lead to continuous tweaks that, over time, can result in significant overall improvements.
- Focus on Customer Value
- Focus on Customer Value
You’ve probably heard the saying, “Customer is King,” right?
Lean project management always prioritizes customer needs. So, ask yourself, “Does this action add value for the customer?”
For example, if a step in your process doesn’t directly improve the product or service for the customer, it may be unnecessary. By focusing on customer value, you can eliminate tasks that are not essential and ensure that every action you take leads to better results.
- Implement Visual Management Tools
- Implement Visual Management Tools
Kanban boards or visual task boards are great tools for applying lean principles. They help track work in progress, identify bottlenecks, and maintain a smooth flow of tasks.
Tools like Meegle are examples of visual management that allow teams to see all ongoing work, who’s responsible, and what stage each task is at. These boards can also help prevent task overload by limiting the number of tasks in progress.
- Standardize Processes
- Standardize Processes
Create standardized procedures for recurring tasks. This reduces variation in workflow and ensures that everyone follows best practices.
For instance, if your team follows a set process for quality checks, you can reduce errors and improve product consistency.
Standardization also makes onboarding new team members easier, as they can follow documented processes instead of learning everything from scratch.
- Engage Your Team in Problem-Solving
- Engage Your Team in Problem-Solving
Lean encourages team involvement in identifying and solving problems. Hence, ensure everyone in your team has a voice in suggesting process improvements.
When a challenge arises, gather input from the entire team to brainstorm solutions. This inclusive approach not only solves issues more effectively but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility across the team.
- Measure and Optimize
- Measure and Optimize
Finally, lean is data-driven.
Set clear metrics to measure success, such as cycle time or customer satisfaction. Plus, regularly review these metrics to see where improvements can be made.
For example, if your project completion times are slower than expected, use data to analyze why and make targeted improvements.
By integrating these lean principles, you can maximize efficiency and continuously enhance the value you deliver. Whether it's through visual management or constant feedback, lean project management keeps teams focused on what matters most: delivering quality results with fewer resources and less time.
How Meegle Helps with Lean Project Management
Implementing Lean principles in project management is about maximizing value and minimizing waste at every step. By focusing on what the customer needs and removing unnecessary actions, Lean project management aligns processes for optimal performance. Meegle’s project management software provides unique tools that naturally complement Lean methodology, from visualizing the value stream to fostering continuous improvement.
Let’s explore how Meegle’s features support the key pillars of Lean project management.
Mapping the Value Stream with Visual Tools
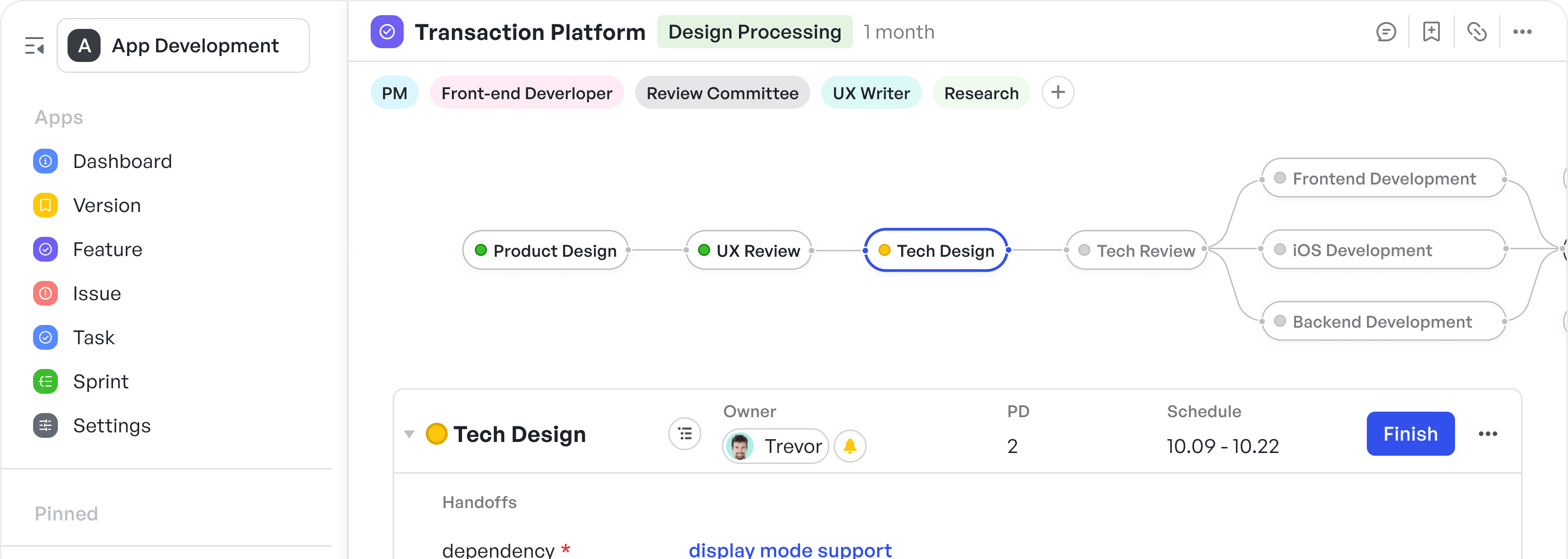
The core of Lean project management is focusing on what adds value to the end product or customer. Meegle supports this by providing a node-driven workflow, where each task or process is represented as an individual “node.” Teams can arrange and connect these nodes to visualize dependencies and flow, making it easier to identify value-adding tasks and remove redundant activities. By clearly illustrating task relationships, Meegle helps teams streamline workflows, allowing them to focus on high-priority, high-impact work.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
Optimize your tasks using Meegle's node driven workflow
Mapping the value stream is fundamental in Lean project management, helping teams identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies within workflows. Meegle’s Tree View provides a multi-level, hierarchical layout that enables teams to visualize workflows and dependencies from a top-down perspective, making it easier to identify waste, such as duplicated efforts or redundant steps, and improve efficiency.
This Tree View also allows for seamless layer-by-layer exploration, letting teams see the big picture with all projects and their current stages. When expanded, it reveals detailed project insights, including task counts, assignments, and progress tracking. This structured view empowers teams to address inefficiencies more effectively, ensuring that tasks are executed smoothly and that value is consistently delivered at every level.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
Fuel progress with the big picture of all the projects with Meegle's Tree View
For teams preferring a more agile, incremental approach, Meegle’s Kanban View allows users to drag and drop tasks between stages, maintaining a real-time understanding of project progress.
This dynamic board layout visually maps each task through the workflow, revealing blockers and ensuring a smooth transition from one task to the next. By viewing the project in terms of stages, Meegle’s Kanban board brings Lean’s value stream principle to life, allowing teams to catch inefficiencies early.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
Manage your project, the agile way with Kanban board
Optimizing Workflow with Pull Systems and Bottleneck Reduction
To maintain an efficient workflow, Lean projects rely on pull systems, which allow teams to “pull” tasks when they’re ready to handle more work. Meegle’s Kanban View facilitates this by letting teams limit work-in-progress (WIP) items, preventing workflow overload and bottlenecks. If a bottleneck does arise, it’s easy to spot within the Kanban or Table views, which makes resolving workflow issues faster.
Facilitating Continuous Improvement with Feedback and Analytics
Lean management is all about continuous improvement, which Meegle enables through its analytics and reporting features.
Teams can monitor key performance metrics, gaining insights that help refine workflows. With real-time feedback, adjustments can be made instantly, allowing teams to stay agile and respond to any changes or challenges as they arise.
Meegle also has out-of-the-box reporting templates with a high level of customization and flexibility. Pie, line, and bar graphs, as well as many other visualization options.
250px|700px|reset
加载中,请稍后
Harness instant data insights to gain a competitive edge, optimize operations, and capitalize on emerging opportunities
Get Lean with Meegle
Meegle makes it easy for teams to embrace Lean project management with tools designed to eliminate waste, streamline processes, and maximize impact.
With features that support every aspect of Lean—value identification, workflow visualization, pull systems, continuous improvement, and collaboration—Meegle is an ideal platform for teams aiming to operate at peak efficiency.