5 Product Backlog Examples Agile Teams Can Use Right Now

A product backlog is a structured list of features, enhancements, and fixes a team needs to apply. It is the single source of truth for development priorities, helping teams focus on the most impactful tasks. Without a clear backlog, projects can lose direction, and critical tasks may be overlooked.
Let’s say you’re part of a startup developing a mobile banking app. You have a long list of things to do, like setting up user authentication or enabling instant money transfers. If you don’t prioritize that list, your team might end up working on lower-priority features, which could delay your app’s launch.
A well-organized backlog solves this problem by ranking tasks based on value, dependencies, and feasibility. This ranking makes it easier to break down big tasks into manageable steps. As a product manager, you can then refine work items, adjust priorities, and plan sprints more effectively.
In this article, we’ll walk through examples of different types of product backlogs to help you organize your workflow and keep your development efforts moving forward.
5 examples of a product backlog done right
A well-structured backlog includes key items that guide Agile teams in delivering valuable features while keeping the product stable. To maintain a balanced backlog, product managers must continuously prioritize tasks based on importance and relevance. Each item should contribute to progress without overcomplicating the planning process.
 Meegle - product backlog management tool
Meegle - product backlog management toolMeegle is an all-in-one project management tool that helps teams organize their backlog with Kanban Views and prioritization tools. It provides a central space where team members can add features, discuss tasks, and decide their importance based on goals and customer feedback.
Get Full Access for Teams of 20, Free Forever!
Here are some key types of product backlog examples used in project planning and development:
Example #1: A backlog with the right sections
Managing a product backlog effectively is a tough job. You're constantly switching between multiple tasks, features, bug fixes, and research, all of which must be handled on time.
You may not always know which items need immediate attention or which should be scheduled for a future sprint. Sometimes, it’s even hard to tell whether a particular task is more important than others because everything is just lumped together. Without proper organization, that growing list can quickly become a massive to-do list that’s hard to manage.
So, how can you avoid all this chaos?
The answer lies in breaking down your backlog into organized sections. Each section serves a specific purpose, making it easier to track progress, assign priority, and set clear expectations.
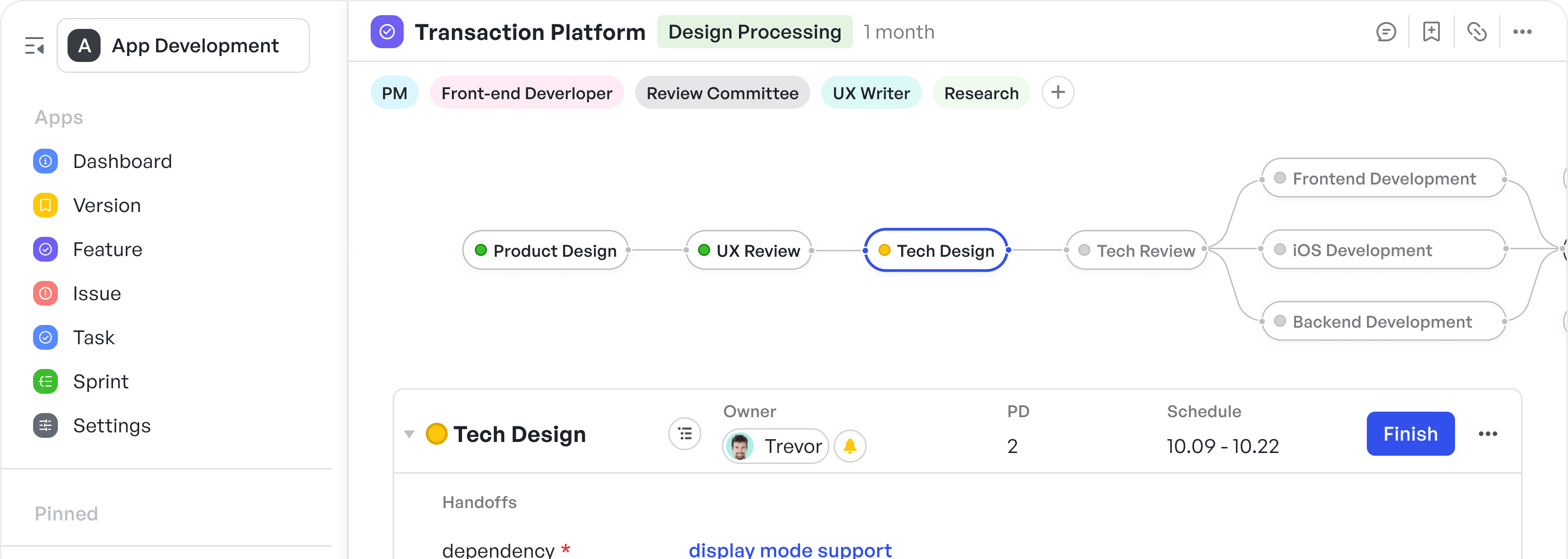
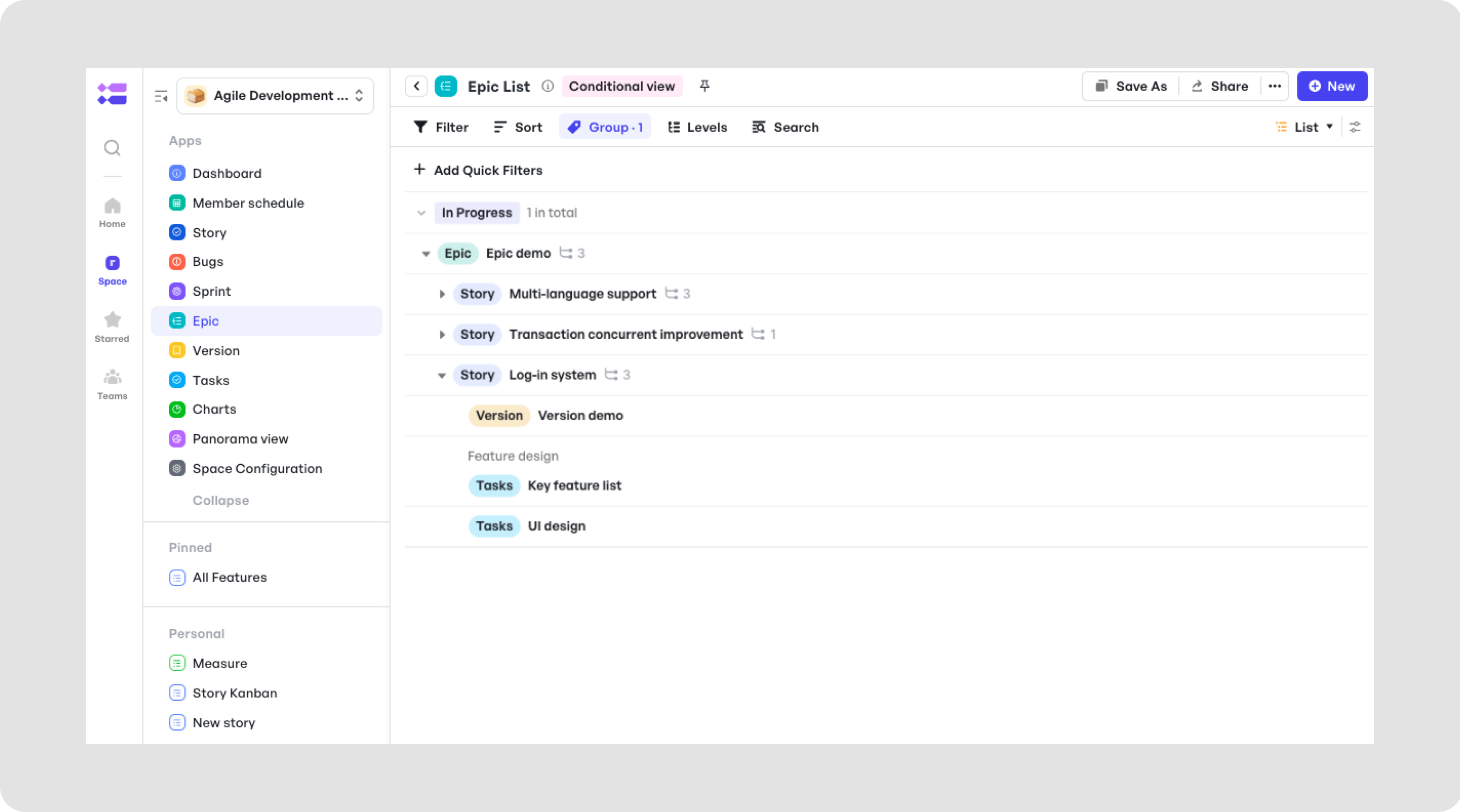 Break down tasks easily into different sections
Break down tasks easily into different sectionsFor instance, if you take a look at the above example, you can use Meegle to break tasks down into Epics, Sprints, and Stories. This will allow you to plan and execute your work effectively.
- Epics represent larger goals or features that require multiple sprints to complete.
 Focus on time-based tasks to drive progress and achieve project milestones in each sprint
Focus on time-based tasks to drive progress and achieve project milestones in each sprint- Sprints focus on time-based tasks and are typically two to four weeks long, during which the development team works to implement and deliver a discrete product increment, serving as a working milestone version. It's a dedicated phase to complete a set number of items that contribute to the overall project.
- Stories are smaller, more actionable tasks that make up the larger Epics, helping you focus on specific, achievable goals within each sprint.
You can manage the entire lifecycle of user stories with Meegle's Agile Development Template, from inception to completion.
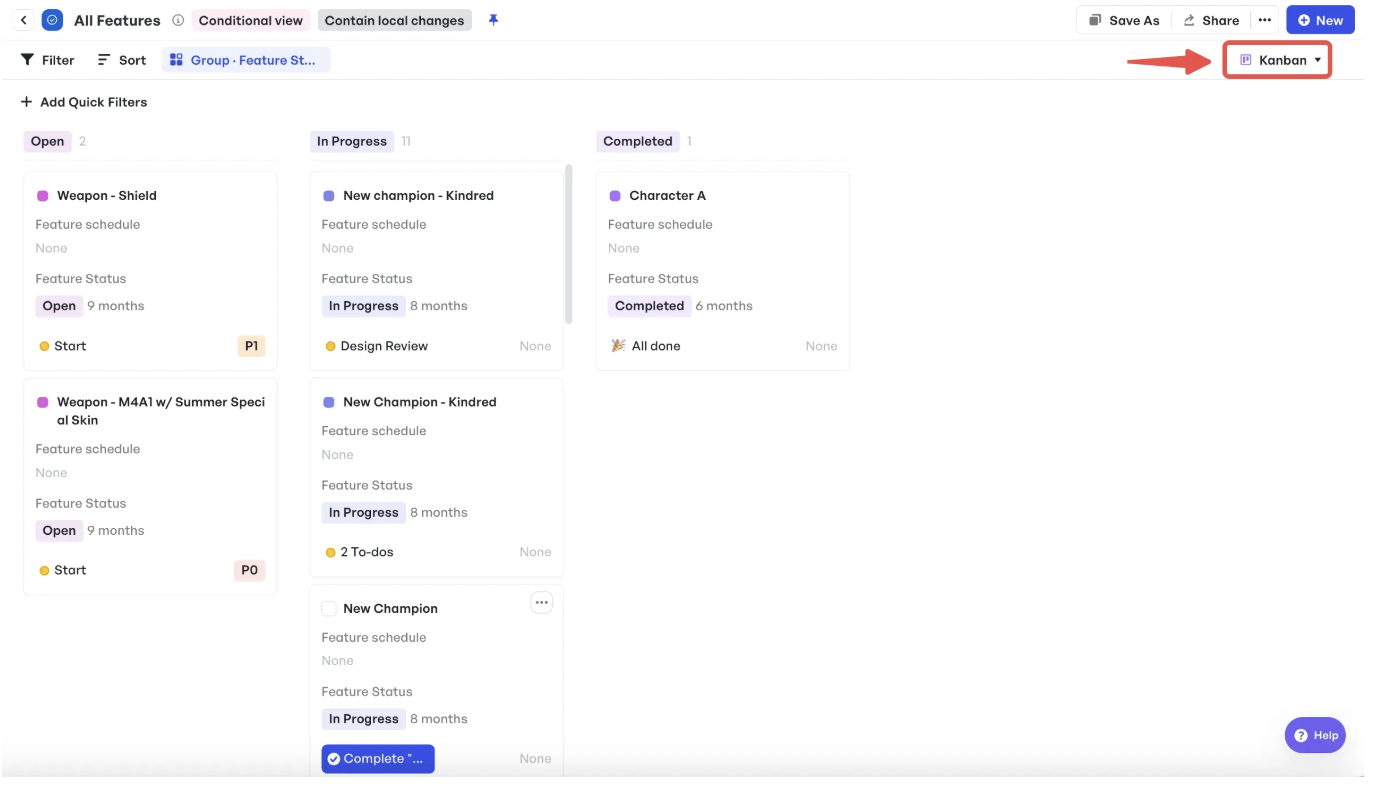 Track the status of each task within the Kanban board
Track the status of each task within the Kanban boardIf you’re a fan of Kanban boards, you know they are a powerful tool for visualizing and managing your backlog. With Meegle’s Kanban boards, you can track the status of each user story at a glance.
These boards provide a clear view of the progress of each task, whether it’s in the "Open," "In Progress," or "Completed" stages. This way, you can quickly identify which stories need attention or adjustments. If you're working on multiple sprints or have many tasks in the queue, this visual approach helps to declutter your mind and your backlog.
You can also access different visualization options like Gantt Charts, which give a clear view of your entire development roadmap. This makes it easy to see how user stories integrate into the larger project, track dependencies, and visualize milestones in real time.
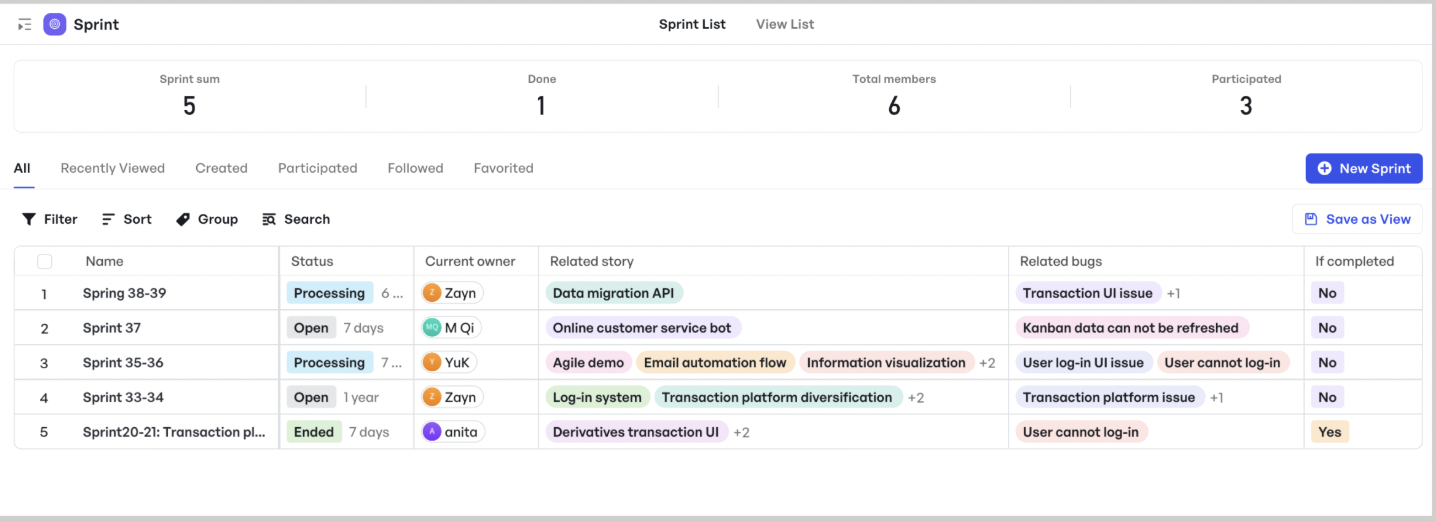
Example #2: A backlog with items in the correct priority order
When you're working with a large backlog, rearranging tasks can take a lot of time if the tools you're using aren't flexible. Maybe a task should move up as a priority, or perhaps you've realized that the task order doesn't make sense anymore.
Meegle solves this by allowing you to create multiple views within your workspace to enhance productivity. You can switch between Table, List, Gantt, Kanban, Tree, and Panorama views, adapting to your workflow:
- List view: A structured and easy-to-read format that provides a complete list of tasks, allowing users to sort and filter based on specific criteria.
- Table view: A detailed display of task requirements, including business line, priority, owner, and nodes in progress. You can edit requirements and update status directly in this view.
- Kanban view: A visual layout that organizes work items by status, allowing users to move tasks between stages based on project progress.
- Gantt view: A timeline-based bar chart that illustrates project progress, showing work item schedules, sprint deadlines, dependencies, and workload distribution.
- Panorama view: A high-level overview that integrates data across teams, providing transparency and stakeholder alignment for better strategic decision-making.
Meegle’s schedule management mode within the Tree View offers a clear view of the entire project. It displays timelines, status, and workload in a hierarchical structure that breaks tasks into smaller, manageable components. This makes it easy to assess overall progress and track key project data, such as deadlines and dependencies.
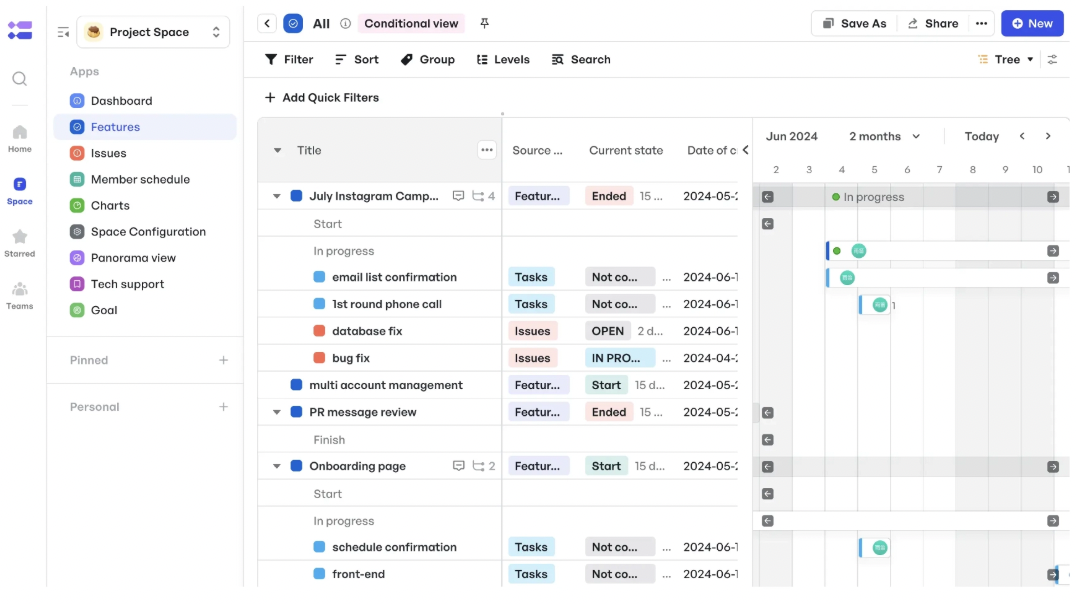 View your projects using the Schedule Management mode in the Tree view
View your projects using the Schedule Management mode in the Tree viewFor task tracking, you can also access a user-friendly interface to visualize what’s completed, what’s pending, and what may be at risk.
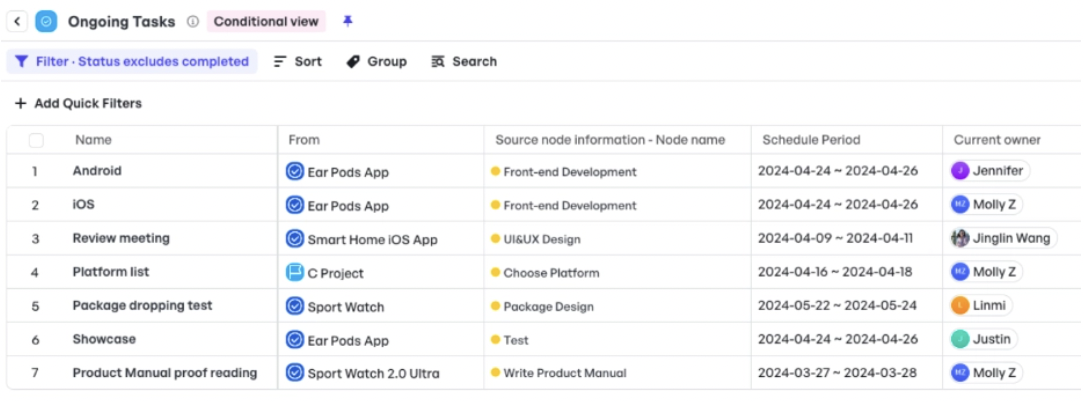 See the status of your project tasks within Meegle
See the status of your project tasks within MeegleExample #3: A backlog with tasks categorized by bugs and issues
When you don’t categorize tasks properly in your backlog, it can be difficult to prioritize what needs attention first. Critical bugs get buried under feature requests, while minor issues take up time that should be spent on urgent fixes.. This lack of organization slows down development.
But beyond just workflow inefficiencies, it contributes to technical debt, making future development more complex and costly. When technical debt piles up, your team ends up spending more time firefighting rather than innovating.
When you categorize tasks into bugs, issues, and new features, you can quickly identify urgent fixes, allocate resources effectively, and keep track of issue resolution.
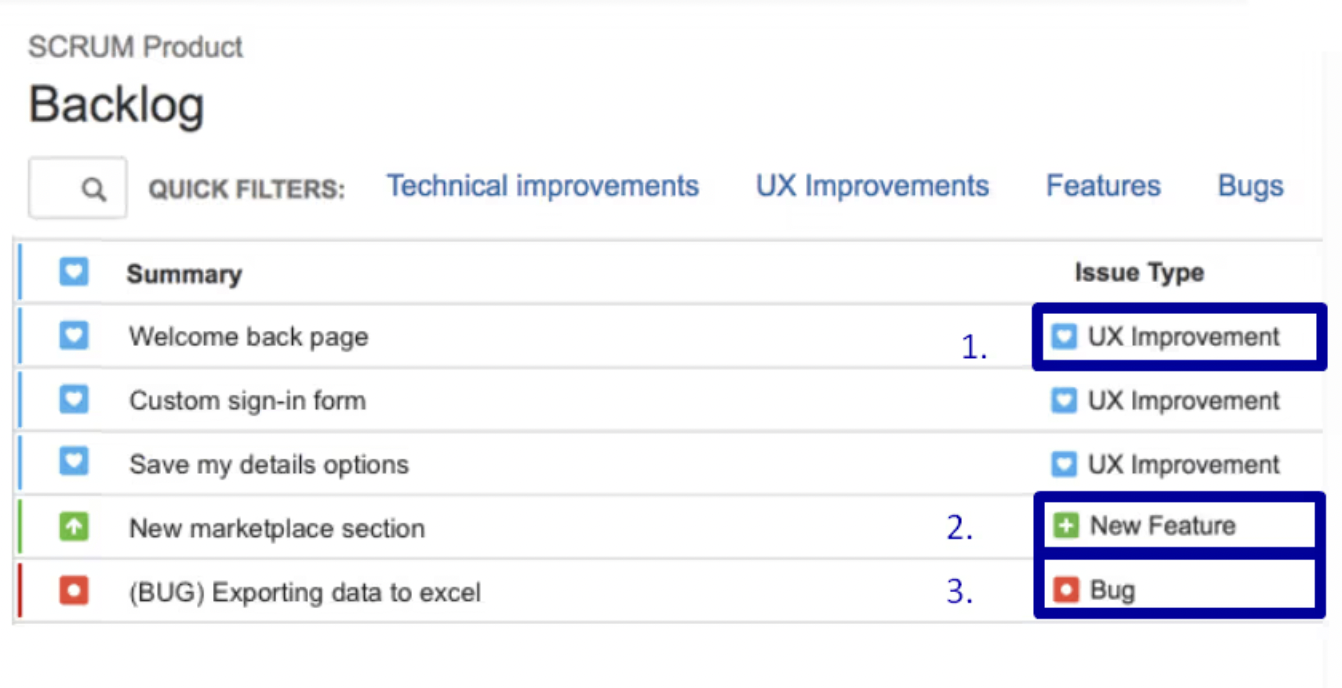 Source: Product School
Source: Product SchoolIn this product backlog example (taken from Atlassian), you can see how tasks are neatly categorized into UX Improvements, New Features, and Bugs. This structure makes it easy to filter and manage different types of tasks.
UX improvements help refine the user experience, new features introduce functionalities, and bugs highlight issues that need immediate resolution.
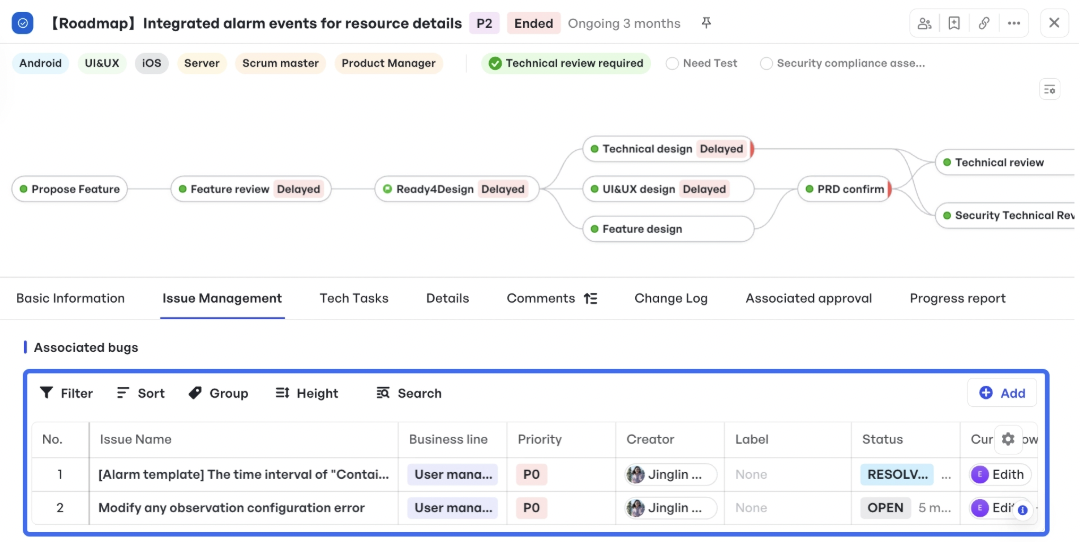 Add and track issues in the backlog
Add and track issues in the backlogIn Meegle, you can easily add and track issues in the Kanban backlog, categorizing and prioritizing bugs based on their impact and urgency. You can also see the status of each issue, whether it's "Resolved" or "Open," for clear visibility into task progress. This helps the team stay aligned so that high-priority issues are tackled first.
Example #4: A backlog optimized for research and experimentation tasks
When your team is dealing with time-bound research and experimentation tasks, traditional backlog management may not always be enough. These tasks often don't fit neatly into typical sprint cycles, but they still need to be tracked, prioritized, and completed in a structured manner.
In such cases, it’s crucial to have a system that allows flexibility. Research tasks might involve exploring new technologies or validating user assumptions, both of which can be time-consuming and require iteration. Experimentation tasks may involve A/B testing or assessing new features to measure their impact. Both categories need to be separated and managed in ways that reflect their unique nature.
For example, in Meegle, you can manage these types of tasks using its reporting and tracking features. Within the dashboards, the cumulative flow diagram provides visibility into task statuses, allowing teams to visualize progress as work moves through different stages. This helps identify issues and potential delays in real time, making it easier to manage timelines effectively.
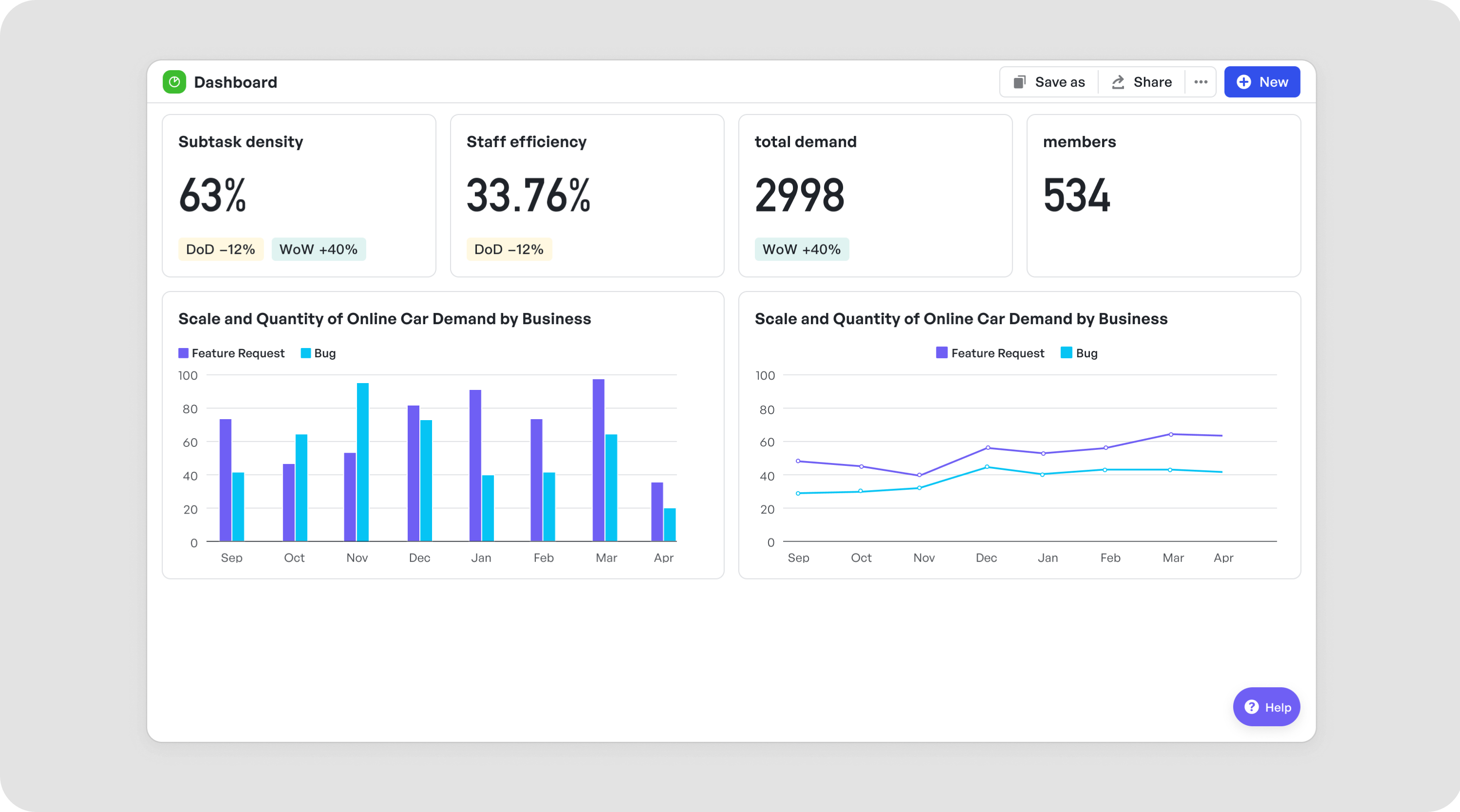 Gain instant data insights and keep stakeholders informed
Gain instant data insights and keep stakeholders informedThe work in progress (WIP) trend shows the completion rates and overall workload at any given moment, offering a clear picture of how tasks are progressing and helping balance resources. The priority distribution chart also provides a comprehensive overview, allowing teams to focus on high-priority items to deliver the most value to users.
Example #5: A backlog that is not cluttered
You may occasionally notice that your backlog is cluttered with outdated tasks, low-priority features, or items that are no longer relevant. When your backlog is full of irrelevant items, it’s tough to figure out what needs to be prioritized and even harder to keep your team focused on the tasks that actually move the project forward.
So, what do you do when your backlog resembles a junk drawer than a productivity tool?
The first step is getting rid of the clutter. Regularly cleaning up the backlog and removing old, outdated items is key to keeping things manageable. Sure, you might have some nice-to-have features you’d love to implement someday, but if they’re not aligned with your current goals, it’s time to let them go.
It’s also common for stakeholders to add items that were important to them months ago but have lost relevance over time. They might still be listed on your backlog, but they haven’t been followed up on, and the chances are high that they’re no longer a priority. In cases like these, don’t hesitate to clear them out. If something hasn’t been revisited, it’s probably safe to assume it’s not urgent.
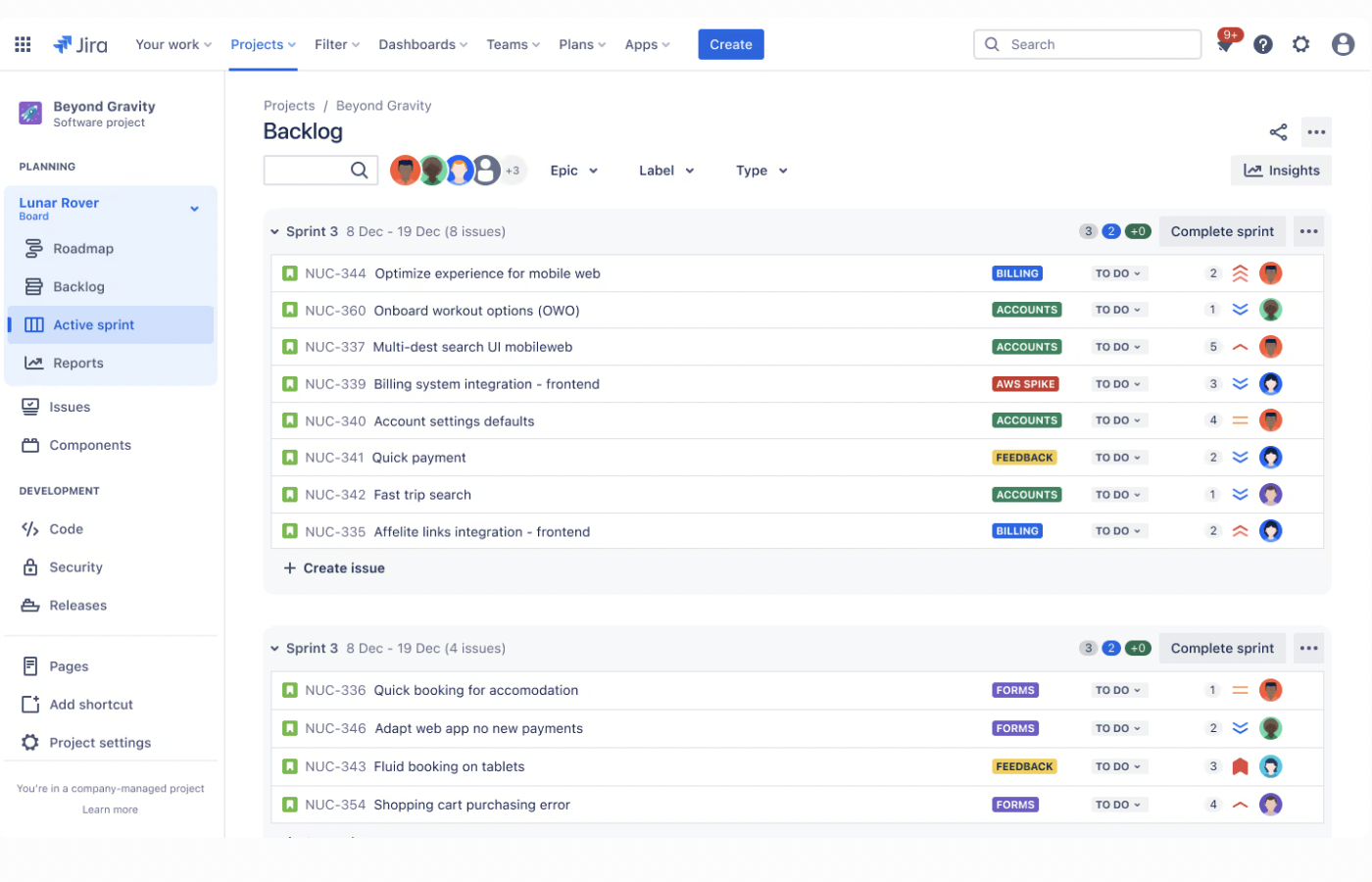 Source: Peakforce
Source: PeakforceIn the above example by Atlassian, you can see what a clean product backlog looks like. Each sprint is well-organized, with tasks categorized and labeled appropriately, and focused on relevant work items. Notice how issues are labeled by category (e.g., Billing, Accounts, AWS Spike), assigned to specific team members, and neatly grouped into sprints.
Keeping your backlog in check is an ongoing process, but when managed well, it becomes a powerful asset that drives focus, efficiency, and successful project execution.
Prioritizing the product backlog: who’s in charge?
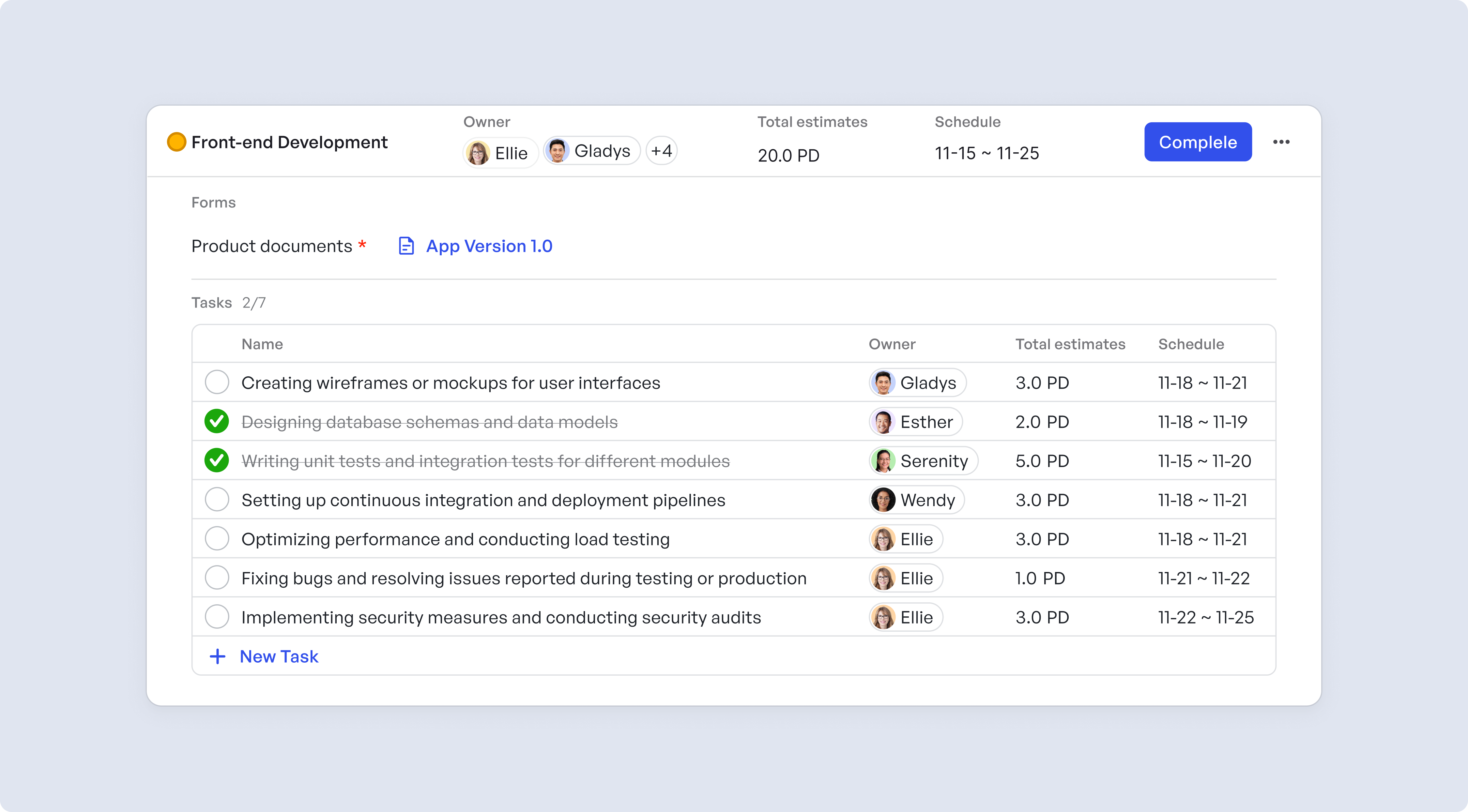 Add and track issues in the backlog
Add and track issues in the backlogTeam members and their tasks Meegle's Agile template
A product backlog drives development by outlining what a team needs to build. On the business side, priorities revolve around three key factors.
- Customer needs and feedback determine which features provide the most value.
- Business goals and market trends guide long-term strategy.
- Finally, technical feasibility and dependencies affect how and when items should be worked.
But who decides what comes first?
In Agile development, the product owner typically prioritizes the backlog, but in some organizations, the product manager takes on this role. Regardless of the role, backlog prioritization is a team effort.
Product roadmap vs product backlog
In product development, a roadmap sets a high-level strategic direction, while the product backlog focuses on the tactical execution of that vision. Though they serve different purposes, both are essential for a product's success.
Here’s a direct comparison of the two:
| Criteria | Product roadmap | Product backlog |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a strategic overview of product goals and vision | Contains detailed, actionable items for development, including features, bugs, and improvements |
| Timeframe | Focuses on the long-term vision (months to years) | Focuses on the short-term planning and execution (sprints or iterations) |
| Ownership | Owned by executive teams or product leadership | Managed by product managers and development teams |
| Scope changes | Relatively stable, with adjustments made based on business goals and market conditions | Frequently evolves, with tasks reprioritized based on feedback and new insights |
Best practices for managing a product backlog example
A well-structured and continuously managed product backlog lays the foundation for efficient product development. Here’s how to do it right.
Prioritize product backlog items with effective frameworks
Backlog items often have varied importance. Choosing a structured prioritization method helps teams decide what gets built first. Different frameworks cater to different needs:
- MoSCoW method (Must-Have, Should-Have, Could-Have, Won’t-Have)
- RICE scoring (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort)
- WSJF (Weighted Shortest Job First)
When using these frameworks to prioritize your work, you’ll have a clear, data-driven approach instead of relying on gut feelings. It will also become easier to move beyond subjective decisions.
But even with these frameworks in place, it's important to consider the business value of each item, the impact on the end user, and the amount of effort required to finish each task.
Regularly review and update the backlog
A product backlog isn’t static, and it requires constant attention. Regular backlog grooming (refinement) keeps tasks relevant, well-defined, and ready for execution.
Here are some tips to keep backlogs updated:
- Remove obsolete items
- Break down Epic-level features into smaller, actionable user stories
- Reevaluate priorities according to market trends and changes in business needs
- Define conditions that must be met before an item is considered complete
Avoid overloading and neglecting backlog refinement
Adding every idea and request to the backlog can be tempting, but an overstuffed backlog becomes overwhelming and counterproductive. It also leads to inefficiency and wasted resources. Regular backlog refinement helps eliminate outdated, irrelevant, or low-priority tasks.
Some of the most common issues include:
- Overloading the backlog, making it difficult to identify priorities
- Skipping backlog refinement, causing confusion and development delays
- Focusing only on new features and ignoring bug fixes and technical debt
- Not considering dependencies
Automate backlog management to improve efficiency
If you manually handle backlog tasks—updating priorities, tracking dependencies, and ensuring stories are development-ready—you’re likely spending more time managing the backlog than actually delivering value. By automating backlog management, you can streamline these processes and focus more on execution.
With Meegle, you can automate workflows based on key events like work item creation, status change, or file value modification. You can also set specific conditions to only automate relevant tasks in the workflow.
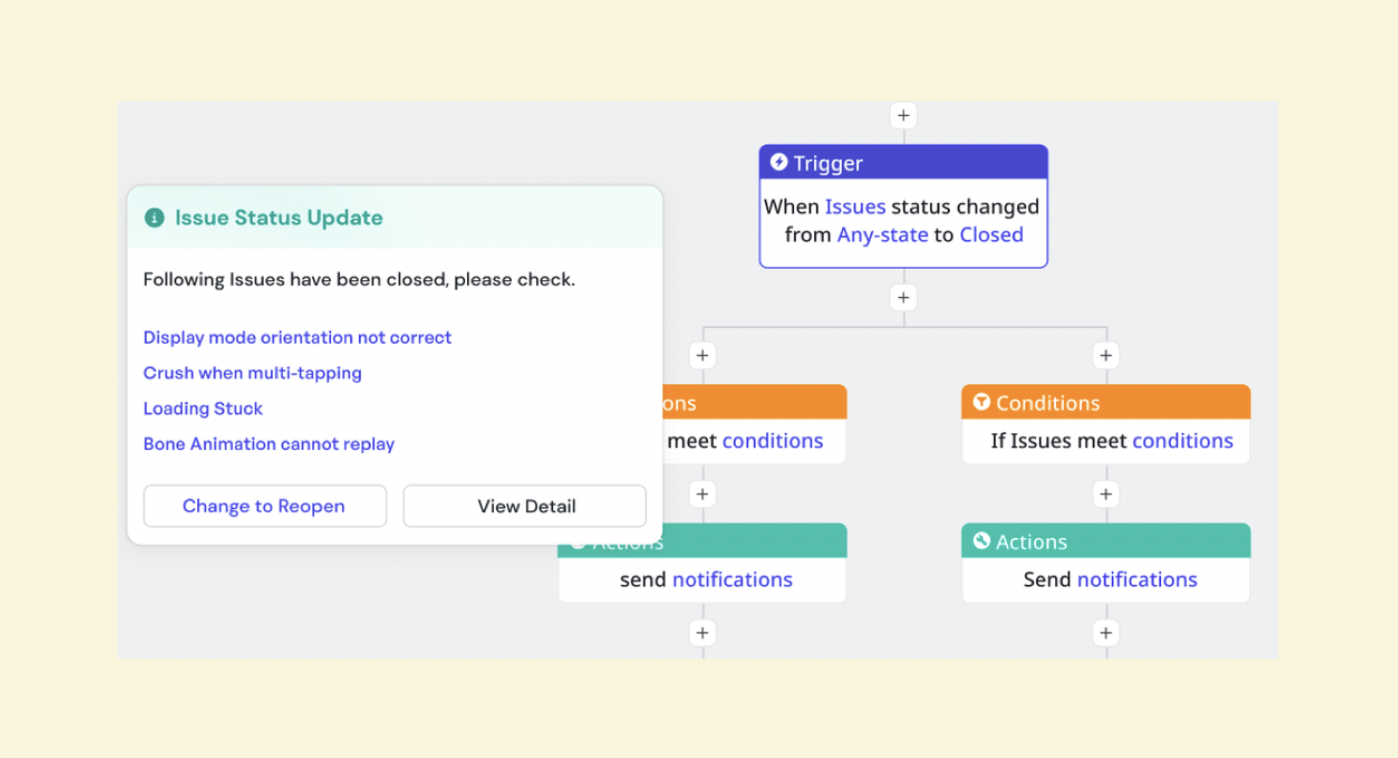 Send notifications automatically for custom triggers within Meegle
Send notifications automatically for custom triggers within MeegleMeegle’s integration with Zapier enhances the platform's functionality by automating tasks and connecting Meegle with over 7,000 apps. You can set up triggers to automatically create tasks in Meegle when you receive an email related to infrastructure updates or when a specific form is filled out (e.g., a system alert form).
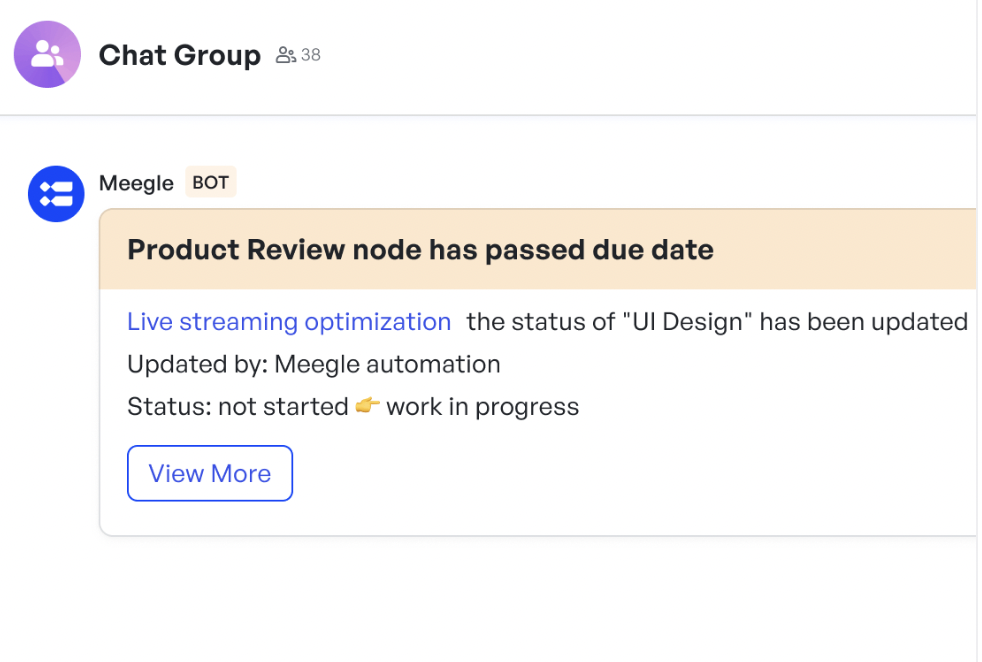 Remind the node owner of the due date of a particular task
Remind the node owner of the due date of a particular taskCustom actions simplify backlog management further, sending notifications, updating fields, creating groups, or adjusting project nodes. For example, Meegle can automatically send a due date reminder to the node owner and associated group one day before a feature’s estimated completion, keeping teams on track.
Manage product backlogs effectively with Meegle
While it’s technically possible to build a product without a backlog, the difference becomes clear when you compare teams that use one with those that don’t. Those with a well-maintained backlog can build more efficient, user-centric solutions and launch them on time, ultimately achieving higher product success.
With Meegle, you can centralize all the information about your product in one place, making it easier to track and manage every aspect of development. It helps you manage Agile projects efficiently, keeping your sample product backlog aligned with evolving priorities.
Try Meegle’s Free Forever Plan and experience how seamless product backlog management can be!
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today